
The MIN is an Excel statistical function that returns the smallest number in a set of values. It will ignore logical and text values. It is one of the oldest Excel functions, so it can be used even with Excel 2003.
If you want to include logical values, you’ll need to use the MINA function.
MIN Syntax
MIN(number1, [number2], ...)
Required Arguments
number1: Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers, which means 8, C2 and D2:D4 are all valid examples.
Optional Arguments
number2-255: You can use up to 255 numbers in the calculation by following the syntax listed above.
Note: If the argument does not contain any numbers, it will return 0.
MIN Function Examples
Get the Smaller Number of Two Values
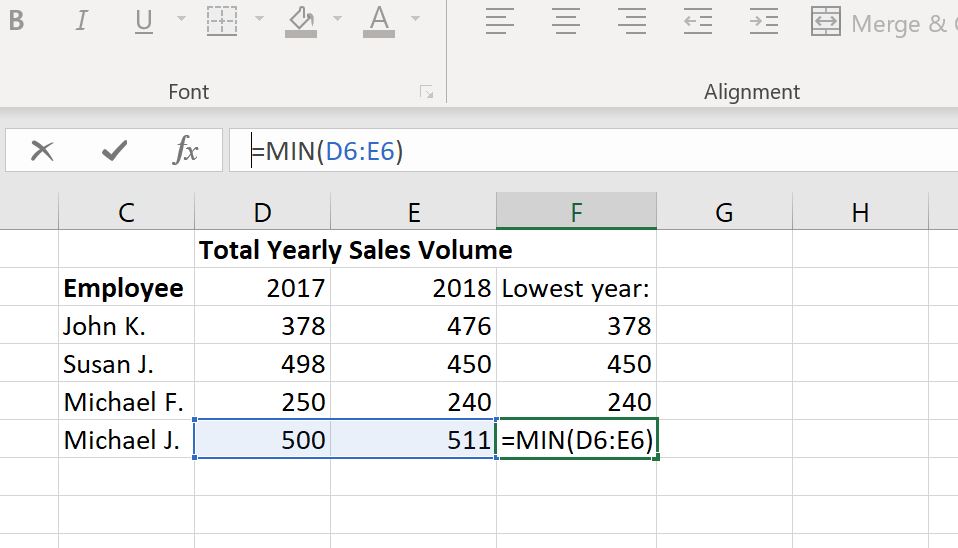
MIN can be used to compare two numbers in a table and return the smaller one. For example, if you want to compare last year’s sales volume to this year’s for every employee and get the smaller value. I’ve added an example screenshot below.
You can also write this as =MIN(D6, E6).
Get the Smallest Number from a Range
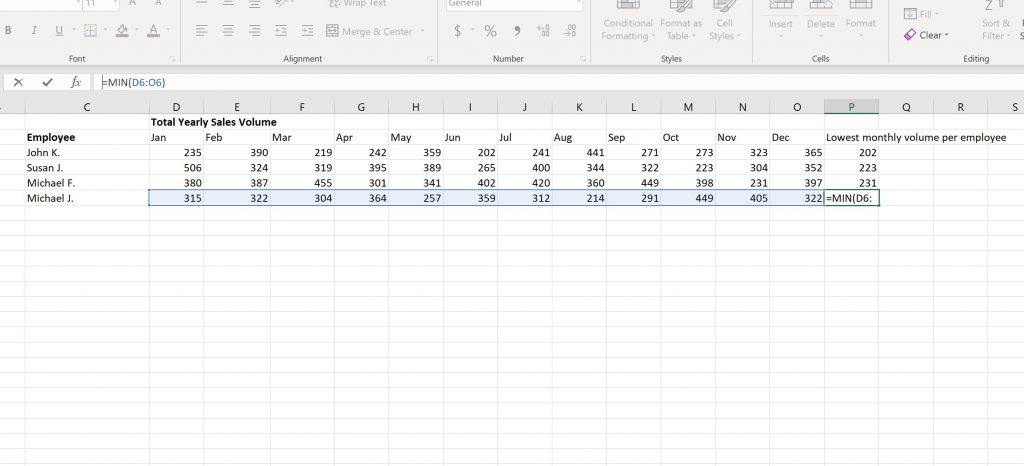
In many cases you might need to find the smallest number from a range in an Excel sheet. If we continue with the sales volume analogy, you can use the MIN function to return the lowest monthly sales per employee.
Using MIN with Mixed Values
The MIN function can also be used with mixed arguments. For example MIN(A3:A6, F7, 345) is perfectly valid and will find the lowest value from the range, cell reference and number and return the smallest from all three.
More Examples and Use Cases
We don’t have any use cases for this formula on our website at this moment but will link them below once we have. Stay tuned!
